
 0 saved
0 saved
 13.6K views
13.6K views








Read this before you over-invest in the latest tech platform, decide to lease rather than buy that new computer, or expect to resell your smartwatc ...
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.




- Consider leasing tech.
A common application of Moore’s Law for many individuals and ...
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Moore’s Law is not a law in a scientific sense, more an observation and predictive mental model. To that end, some have argued that it is self-fulfilling, with companies feeling the need to keep up with Moore’s law — though that seems like less of a limitation and more of a complement.
Causal relationships aside, many argue that Moore’s Law is coming to its end because of the challenges to build smaller circuits, as the amount of energy needed to cool down the transistors will become larger than the amount of energy already passing through the transistor.
However, that has been a point of debate when taking Moore’s Law as a loose definition of exponential growth. While computers won’t necessarily improve in the ways Moore originally referenced, advancements in cloud computing, quantum physics and the internet of things are likely to create other forms or rapid development.
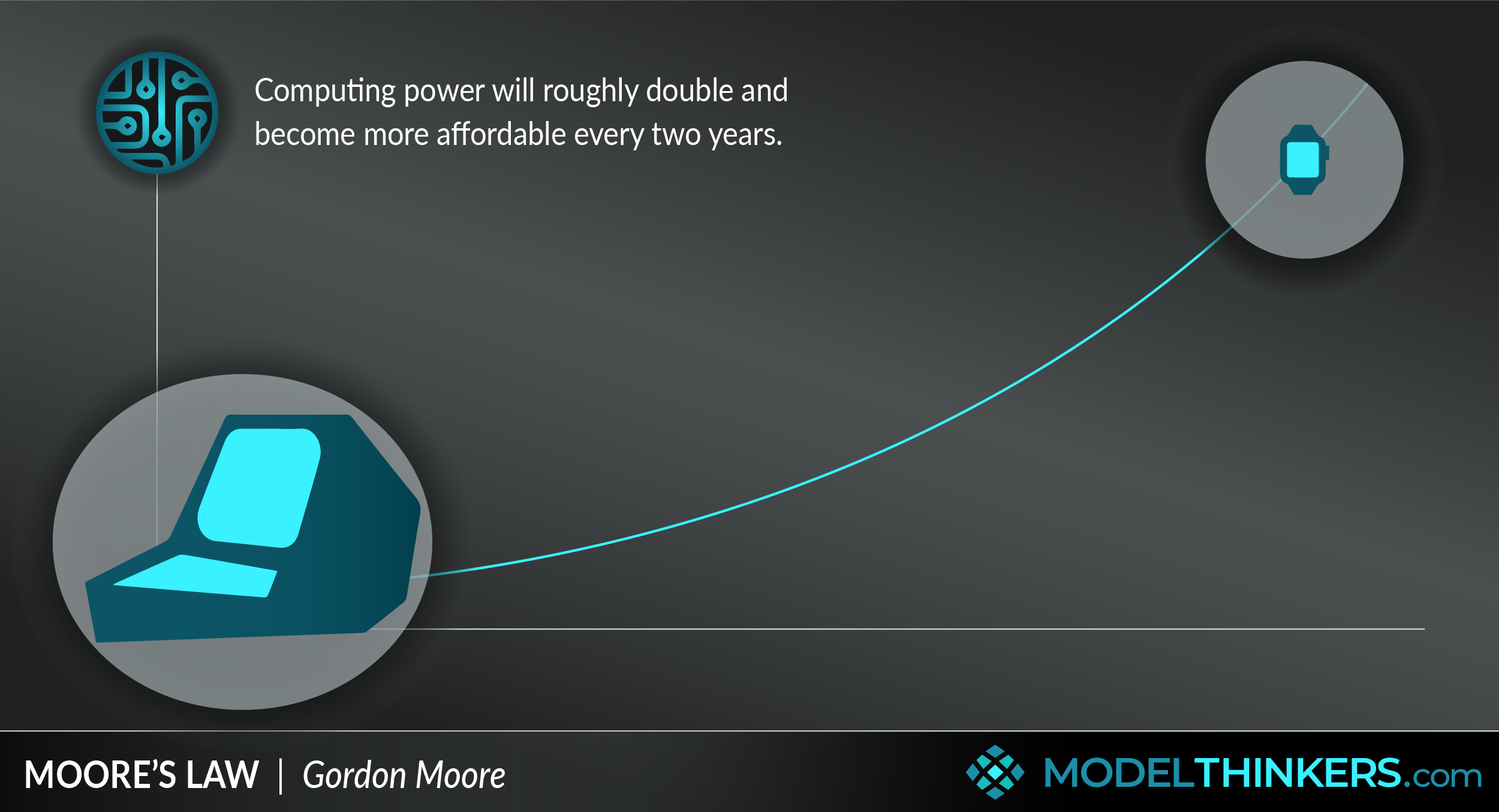
Your USB stick vs Apollo 11 mainframe computer.
It’s not just your smartphone that is more powerful than the old supercomputers, this ZME Science article notes that even a USB stick or WiFi router is technically more powerful than the 1969 mainframe computers used to guide the first rocket to the moon.
The reducing cost of technology.
Jerrold Siegel from the University of Missouri, notes in this article that: “A computer chip that contained 2,000 transistors and cost $1,000 in 1970, $500 in 1972, $250 in 1974, and $0.97 in 1990 costs less than $0.02 to manufacture today A personal computer that cost $3,000 in 1990, $1,500 in 1992, and $750 in 1994 would now cost about $5.”
Moore’s law is a model used to understand the rapid development of technology.
Use the following examples of connected and complementary models to weave Moore’s law into your broader latticework of mental models. Alternatively, discover your own connections by exploring the category list above.
Connected models:
- Compounding: to understand the exponential growth element of Moore’s law.
- Red queen effect: understanding the pace of movement in the broader industry.
Complementary models:
- Zawinski’s law: in understanding expectations for faster development of broad solutions.
- Opportunity cost: to consider the alternative costs of commiting to technology solutions without a view to their potential obsolescence in the medium term.
- The Lindy effect: perhaps a counter to the wisdom that past time can predict future longevity.
This law was inspired by Gordon Moore, co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and CEO of Intel. He made the observation in 1965 when he projected the rate of growth for another decade and has expressed surprise at how long the phenomena has persisted.
Find out more in Moore's Law: The Life of Gordon Moore, Silicon Valley's Quiet Revolutionary by Arnold Thackray, David Brock, and Rachel Jones.
Also, consider whether some have been too quick to claim that Moore’s law is dead by viewing this in-depth opinion piece in Venture Beat.
 My Notes
My Notes
Oops, That’s Members’ Only!
Fortunately, it only costs US$5/month to Join ModelThinkers and access everything so that you can rapidly discover, learn, and apply the world’s most powerful ideas.
ModelThinkers membership at a glance:






“Yeah, we hate pop ups too. But we wanted to let you know that, with ModelThinkers, we’re making it easier for you to adapt, innovate and create value. We hope you’ll join us and the growing community of ModelThinkers today.”