0 saved
0 saved
 18.6K views
18.6K views








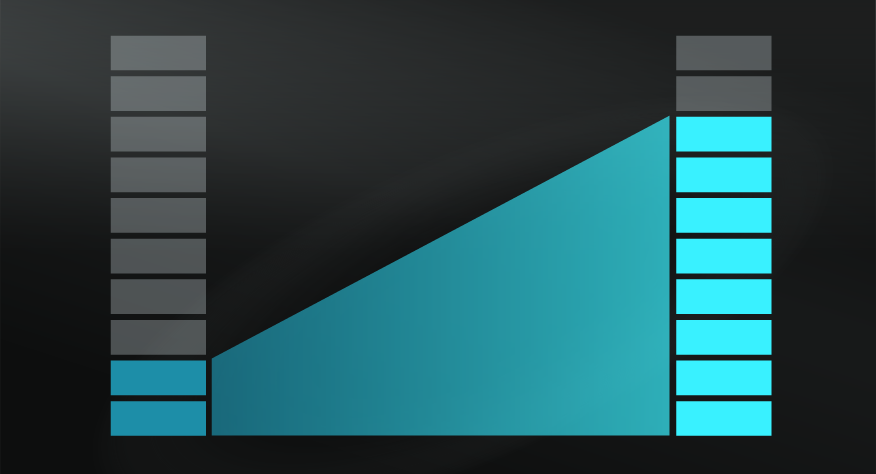
Just in case you were becoming too accustomed to the anxiety of living in a complex world, use this model to appreciate it's real volatility.&n ...
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.




- Embrace unpredictability and ambiguity
The butterfly effect is another reminder that, even within system ...
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Curabitur pretium tincidunt lacus. Nulla gravida orci a odio, et viverra justo commodo id. Aliquam in felis sit amet augue laoreet fringilla. Suspendisse potenti. Sed in libero ut nibh placerat accumsan. Proin ac libero euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt. Aenean euismod, nisi vel consectetur interdum, nisl nisi cursus nisi, vitae tincidunt nisi nisl eget nisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Vivamus lacinia odio vitae vestibulum. Nulla facilisi. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Nam sit amet erat euismod, tincidunt nisi a, tincidunt nunc. Sed sit amet ipsum non quam tincidunt tincidunt. Nulla facilisi. Donec vel libero nec justo tincidunt tincidunt. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Integer in libero ut justo cursus tincidunt. Sed vitae libero sit amet dolor tincidunt tincidunt.
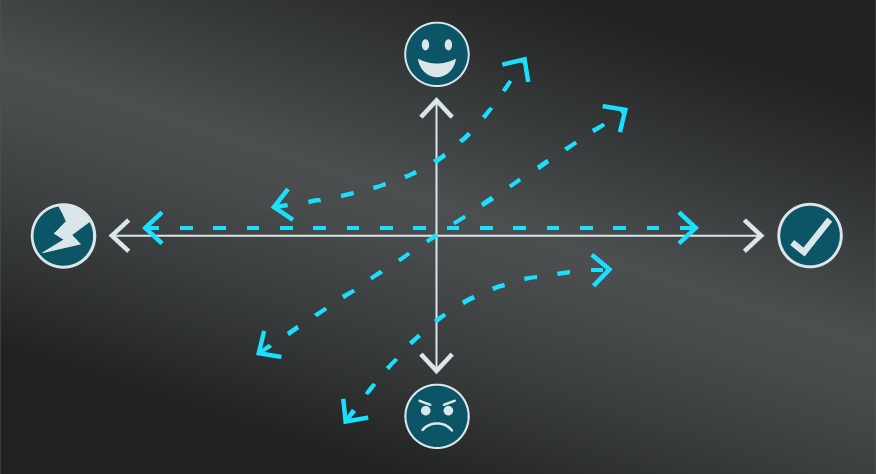
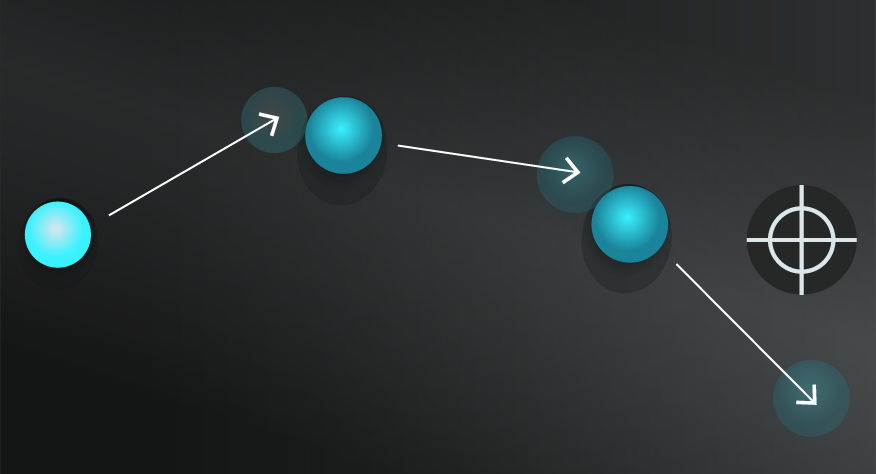
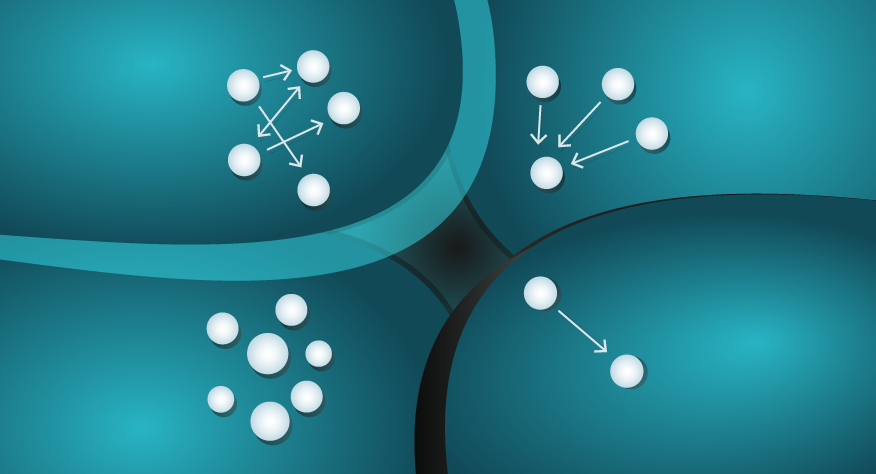
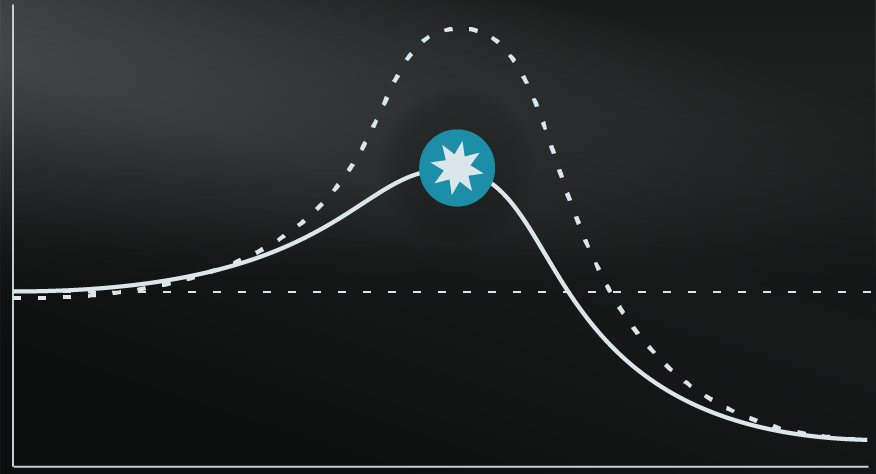
The Butterfly Effect tends to be misunderstood in popular culture. The idea of a butterfly flapping its wings and causing a typhoon is fascinating but has been interpreted as a linear explanation behind major events, rather than the intended emphasis towards complex and unpredictable patterns.
It should also not be interpreted as arguing that minor changes always have major impacts. Sometimes a butterfly will flap its wings and there will be no perceivable impact on a complex system. Sensitivity is in itself unpredictable.
Thus, one criticism of the Butterfly Effect might be the ‘so what?’ If we embrace the unpredictability that it argues, what can we do with that, how do we plan, how do we trust any other model, theory or prediction? However, a more balanced view would see it as a grounding warning.
A Butterfly Effect at Twitter
Twitter founder and CEO Jack Dorsey has discussed the impact of early decisions on Twitter. In a podcast interview, Dorsey explained he would have hired “a game theorist to just really understand the ramifications of tiny decisions that we make, such as what happens with retweet versus retweet with comment and what happens when you put a count next to a like button?”
He attributes that early decision and it’s implicit rewarding of liked and shared content over other metrics such as diversity, accuracy or relevance, with the ‘clickbait’ and sensationalist culture found in some parts of Twitter.
His plan for the future embraces this unpredictability — advocating a considered and iterative approach that embraces the scientific method to continually improve the product and experience.
The butterfly effect points to uncertainty and unpredictable complex systems.
Use the following examples of connected and complementary models to weave butterfly effect and chaos theory into your broader latticework of mental models. Alternatively, discover your own connections by exploring the category list above.
Connected models:
- The ripple effect, avalanche effect and domino effect: all similar mental models pointing to the exponential impact of small factors, though they don’t emphasise the unpredictable and nonlinear nature of chaos in the same way.
- The map is not the territory: another reminder that our simplified understanding of reality are in fact not reality.
- Black swan events: linked to major events taking us by surprise and how we react and want to explain them afterwards.
- Catalyst: similar mental model with a minor element promoting change at a large scale.
- Compounding: speaks to the exponential impact of a small starting point.
Complementary models:
- Diversification: in an unpredictable world best be prepared for, well, unpredictability.
- Leverage: not to be mistaken with the butterfly effect, leverage works with more controlled and predictable elements to create an amplified impact.
- 4Ps of marketing: aim to apply small improvements to these factors to test long term impact.
- Scientific method: use this method to continually test and update understanding in a complex world.
- Occam’s razor: sometimes it wasn’t the butterfly flapping, sometimes it was just a more direct and obvious causal relationship.
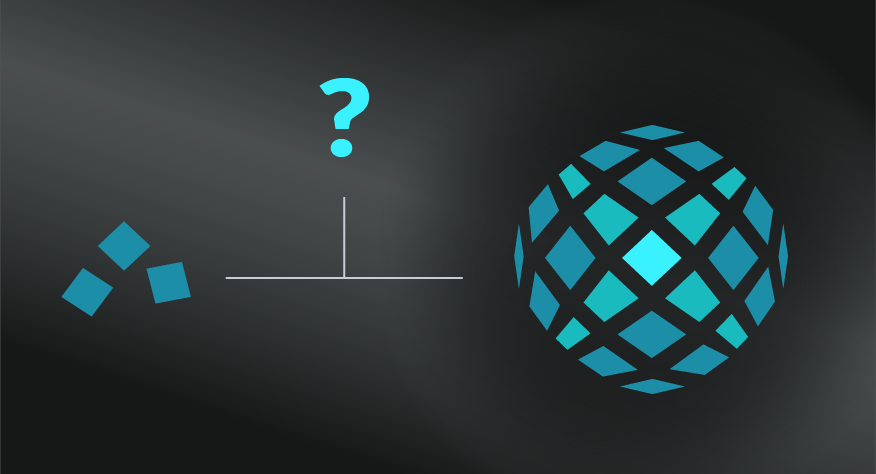
The Butterfly Effect concept was coined by American mathematician and meteorologist Edward Lorenz who imagined the metaphor of a tornado being determined by perturbations as minor as the flapping of the wings of a butterfly weeks earlier.
The idea of small actions having large effects had been described before by many mathematicians and philosophers, with the most famous probably being that of Johann Gottlieb Fichte who said in his 1800 work The Vocation of Man that "you could not remove a single grain of sand from its place without thereby ... changing something throughout all parts of the immeasurable whole".
 My Notes
My Notes
Oops, That’s Members’ Only!
Fortunately, it only costs US$5/month to Join ModelThinkers and access everything so that you can rapidly discover, learn, and apply the world’s most powerful ideas.
ModelThinkers membership at a glance:






“Yeah, we hate pop ups too. But we wanted to let you know that, with ModelThinkers, we’re making it easier for you to adapt, innovate and create value. We hope you’ll join us and the growing community of ModelThinkers today.”